ESS vs BESS: What’s the Difference? The Complete Guide (2025)
ESS vs BESS: As energy storage technologies continue growing across homes, C&I facilities, and utility grids, buyers often ask the same question:
“What is the difference between ESS and BESS?”
Although both terms are related, they are not the same. Understanding the difference helps you choose the right system for backup, solar storage, or off-grid use.
This guide explains ESS vs BESS in a simple, clear way so you can make smarter purchase decisions—especially when comparing products on F2C Deals.
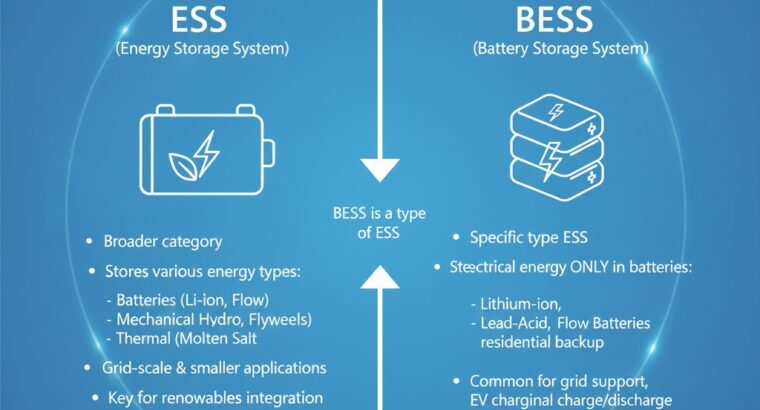
What Is an ESS (Energy Storage System)?
An ESS is a broad term that includes any technology used to store energy for later use.
It can store electrical, mechanical, thermal, or chemical energy, depending on the application.
Examples of ESS technologies
- Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS)
- Thermal storage systems
- Pumped hydro storage
- Flywheel energy storage
- Compressed air energy storage (CAES)
Where ESS is used
- Utility-scale grid stabilisation
- Peak shaving & load shifting
- Renewable integration (solar, wind, hydro)
- Large industrial plants
- Microgrids and remote sites
Because ESS includes many technologies, it is considered an umbrella term.
What Is a BESS (Battery Energy Storage System)?
A BESS is a type of ESS that specifically stores energy using batteries.
Most modern BESS solutions use Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries due to high safety and long cycle life.
Core components of a BESS
- Battery modules or battery racks
- Battery Management System (BMS)
- PCS / inverter
- EMS (Energy Management System)
- Fire suppression & safety systems
- Enclosure (cabinet, container, wall-mounted housing)
Types of BESS
- Portable BESS – camping, outdoor, backup
- Residential BESS – home solar storage
- C&I BESS – factories, telecom, warehouses
- Containerized BESS – utility & large-scale applications
You can explore different types and uses of BESS in more detail on Sunlith Energy
👉 https://sunlithenergy.com/

ESS vs BESS : Key Differences
Below is a simple comparison to make the differences clear.
1. Scope
- ESS = Broad category
- BESS = Battery-based ESS only
2. Storage Medium
- ESS → mechanical, thermal, chemical, or electrical
- BESS → only chemical (battery-based)
3. Applications
- ESS → ideal for large microgrids, utility storage, industrial load balancing
- BESS → perfect for homes, C&I, EV charging, backup power, solar optimization
4. Cost & Complexity
- ESS (such as thermal or hydro storage) is large-scale and costly
- BESS is modular, scalable, and increasingly affordable for homes & businesses
Why BESS Is More Popular Today
Most new energy projects—especially solar-related—prefer BESS due to:
✔ Quick installation
✔ High safety (LFP technology)
✔ Long cycle life
✔ Works seamlessly with solar inverters
✔ Modular and expandable
✔ AI-enabled EMS for smarter usage (peak shaving, backup, time-of-use control)
Because of these advantages, BESS now dominates residential and C&I projects.
If you want to explore more on BESS, Sunlith Energy provides clear explanations and product insights:
👉 Visit Sunlith Energy
Which One Should You Choose—ESS or BESS?
Here’s an easy way to decide:
Choose ESS if:
✔ You need long-duration storage
✔ The project includes thermal, mechanical, or hydro technologies
✔ Your application is beyond typical battery storage
Choose BESS if:
✔ You want solar + battery
✔ You need fast backup
✔ You need peak shaving or bill reduction
✔ You want scalable and modular systems
✔ You are a homeowner, C&I user, EPC, or integrator
For 90% of modern energy projects, BESS is the preferred solution because it’s compact, modular, and cost-effective.
Real-World Examples
Example 1: Home Solar Setup
A family installs a rooftop solar system.
They add a residential BESS so they can store excess solar energy and reduce grid bills.
Example 2: Telecom Tower Backup
A telecom operator switches from diesel generators to a C&I BESS cabinet to cut fuel costs and ensure reliable uptime.
Example 3: Camping & Outdoor
A traveler uses a portable BESS instead of a noisy generator for charging devices and powering appliances.
All these examples show that BESS is a subset of ESS designed for modern, clean, and efficient energy needs.
Conclusion: BESS vs ESS — Final Summary
- ESS = General term for all energy storage technologies
- BESS = A specific type of ESS that uses batteries
- BESS is growing fastest due to cost, modularity, and flexibility
- Homes, C&I, and renewable developers mainly choose BESS
Understanding the difference helps you select the right technology for your home, solar project, or industrial site.
Leave your comment