Energy Storage Systems (ESS): The Complete Guide for Homes, Businesses & Future Grids
What Are Energy Storage Systems (ESS)?
Energy Storage Systems (ESS) store electricity when power supply is high and release it when demand increases. They make modern energy solutions more stable, reliable, and affordable. ESS supports homes, commercial facilities, industrial plants, EV charging, microgrids, and renewable energy projects.
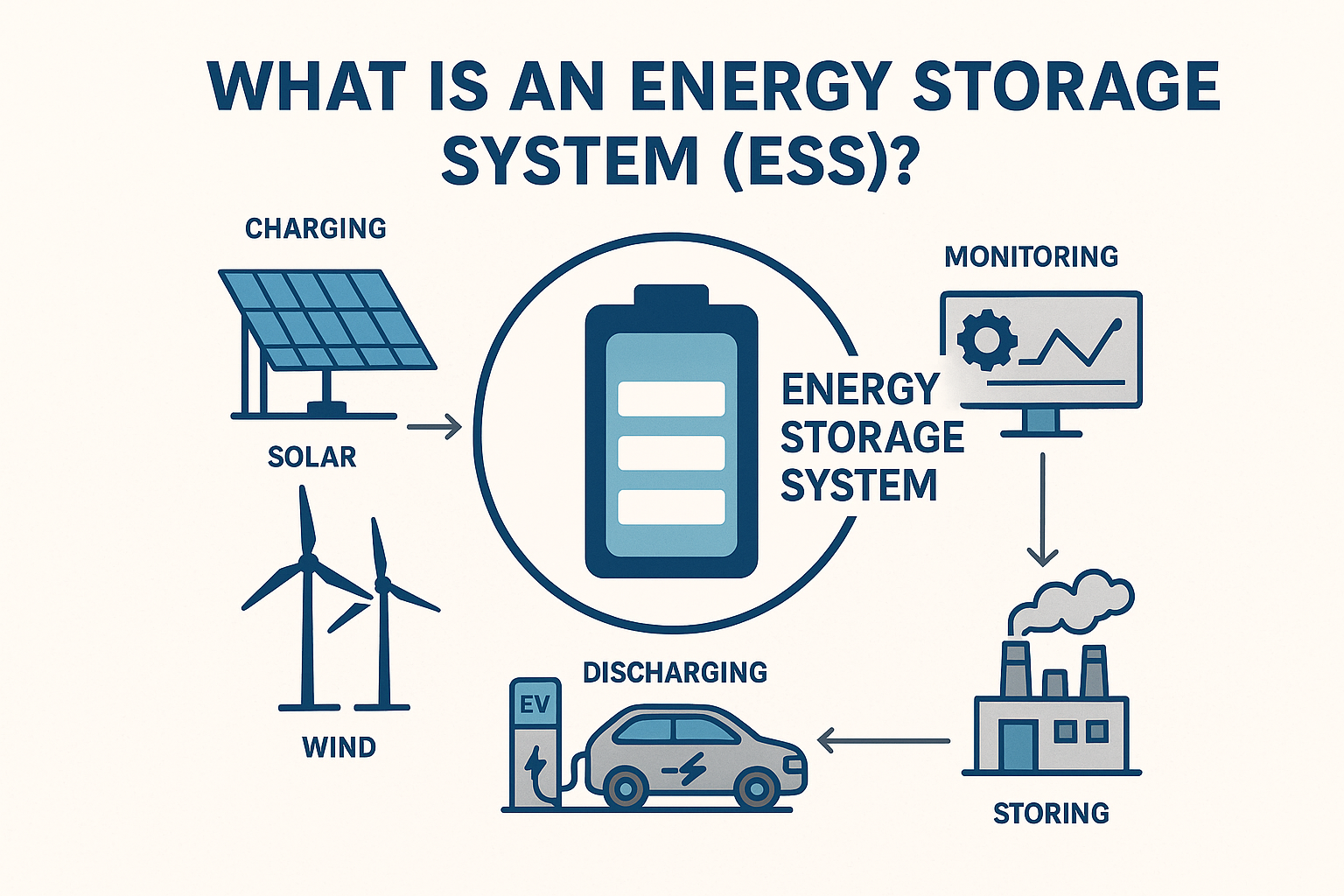
ESS bridges a major gap in renewable power. Solar and wind are clean but intermittent. ESS stores their excess energy and supplies it later, ensuring continuous electricity throughout the day.
Because of this, ESS is now considered the backbone of the future power grid.
Why ESS Matters Today
The world is moving toward electrification. Homes add solar. Businesses shift to clean power. Electric vehicles expand rapidly. All these changes create pressure on power systems.
ESS solves these challenges by providing:
- Stable power during outages
- Lower electricity bills
- Peak shaving and demand management
- Better utilization of solar and wind
- Backup power for critical equipment
These benefits make ESS practical for residential, commercial, industrial, and grid-scale projects.
How Energy Storage Systems Work
Despite the many types, every ESS follows the same basic steps:
1. Energy Input
ESS receives energy from a source such as:
- Solar panels
- Wind turbines
- Grid electricity
- Generators
2. Energy Conversion
A Power Conversion System (PCS) converts AC → DC or DC → AC based on the charging or discharging cycle.
3. Energy Storage
Energy is stored inside:
- Batteries
- Mechanical storage
- Thermal systems
- Hydrogen tanks
4. Energy Output
ESS releases the stored energy when needed. This powers loads such as:
- Homes
- Shops
- Factories
- EV chargers
- Data centers
5. Control & Safety — Managed by EMS
An Energy Management System (EMS) monitors:
- SOC (state of charge)
- Temperature
- Discharge rate
- Load patterns
EMS ensures the system runs safely and optimally.
For a deeper understanding of ESS design, you can explore practical insights from suppliers like Sunlith Energy .
Types of Energy Storage Systems (ESS)
Different Types of ESS. Each Energy Storage Systems type offers unique benefits depending on usage, scale, and performance requirements.

1. Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS)
BESS is the most common and fastest-growing ESS category. It stores energy chemically and releases it instantly when needed.
Popular Battery Chemistries
- Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP)
- NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt)
- Lead-acid (older, less efficient)
- Vanadium Flow batteries (long duration)
Where BESS Is Used
- Homes with solar rooftop systems
- Commercial backup power
- Industrial peak shaving
- EV charging hubs
- Data centers
- Microgrids
- Utility-scale solar + storage
Benefits of BESS
- High efficiency (up to 95%)
- Compact and modular
- Fast charging and discharging
- Long lifespan
- Easy deployment
Why LFP Batteries Dominate
LFP batteries offer high safety, long cycle life, and stable performance. Their price has fallen significantly, making them ideal for homes and C&I projects.
2. Mechanical Energy Storage
Mechanical ESS stores energy in physical form. Key types include:
Pumped Hydro Storage
Moves water between high and low reservoirs.
Best for: Large utility-scale systems.
Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES)
Stores air under pressure and releases it to drive turbines.
Best for: Long-duration, grid-level storage.
Flywheel Storage
Stores energy in a spinning rotor.
Best for: Fast response, power quality, industrial support.
Mechanical storage has capacity advantages but requires specific locations and larger investment.
3. Thermal Energy Storage (TES)
Thermal ESS stores heat or cold. It is widely used in:
- CSP (concentrated solar power plants)
- Buildings and HVAC load shifting
- Food processing
- Industrial heating and cooling
Thermal systems are cost-effective and reliable for heat-based applications.
4. Hydrogen & Power-to-X Storage
Hydrogen storage converts electricity into hydrogen through electrolysis. The hydrogen is stored and later used through turbines or fuel cells.
Where Hydrogen ESS Makes Sense
- Long-duration storage (weeks to months)
- Remote microgrids
- Industrial processes
- Seasonal renewable energy shifting
Though efficiency is lower compared to batteries, hydrogen excels in capacity and long-term storage.
ESS for Different Applications
Below is a practical breakdown of how ESS is used in various segments. This format increases GEO value and improves answer-engine ranking.
ESS for Homes: Residential ESS
Residential ESS usually comes in compact wall-mounted units. It stores solar power during the day and supplies clean power at night.
Benefits
- Reduces electricity bills
- Provides backup power
- Improves solar savings
- Quiet and maintenance-free
The most popular size ranges are 5 kWh–20 kWh depending on home load.
ESS for Businesses: Commercial & Industrial (C&I ESS)
C&I ESS helps businesses reduce energy costs and improve reliability.
Key Advantages
- Peak demand reduction
- Backup power
- Load balancing
- EV charging support
- Better use of rooftop solar
C&I systems typically range from 50 kWh to several MWh.
ESS for Utility-Scale Projects
Utility-scale ESS strengthens the grid by enabling renewable integration.
Roles
- Frequency stabilization
- Load shifting
- Renewable energy smoothing
- Power plant optimization
- Black start capability
These installations can reach hundreds of MWh and support entire regions.
For insights on commercial and containerized BESS solutions, see Sunlith Energy’s engineering overview.
Benefits of ESS Across All Sectors
1. Reliability
ESS ensures continuous power during outages.
2. Energy Savings
Load shifting and peak shaving reduce electricity costs.
3. Renewable Energy Optimization
ESS unlocks full solar and wind potential.
4. Grid Stabilization
Provides fast response and supports frequency regulation.
5. Sustainability
Reduces fossil fuel use and promotes clean energy adoption.
6. Flexibility
ESS fits homes, shops, malls, factories, EV stations, microgrids, and large-scale utilities.
How to Choose the Right ESS(Energy Storage Systems)
Step 1: Identify your load & purpose
- Backup?
- Energy savings?
- Solar integration?
- EV charging?
Step 2: Select the ESS type
- LFP battery for homes
- BESS for C&I
- Hybrid systems for microgrids
- Hydrogen/CAES for long-duration storage
Step 3: Check PCS & EMS compatibility
Step 4: Verify sizing for real load patterns
Step 5: Compare installation & maintenance needs
This guide helps both beginners and professionals make informed decisions.
Future of Energy Storage Systems (ESS)
ESS will continue to grow due to:
- Falling lithium battery prices
- Rising global solar/wind installations
- EV charging expansion
- Smart grids and AI-driven EMS
- Demand for resilient power
Hybrid systems, long-duration storage, and integrated EV + ESS solutions will shape the next decade.
Conclusion
Energy Storage Systems (ESS) are transforming how homes, businesses, and utilities use and store power. ESS enables reliability, cost savings, and renewable energy adoption. Whether you are installing rooftop solar, powering a factory, or designing a microgrid, ESS is the key to a stable and sustainable energy future.
Leave your comment