How BESS Works: Inside the Technology of Modern Energy Storage (2025 Expert Guide)
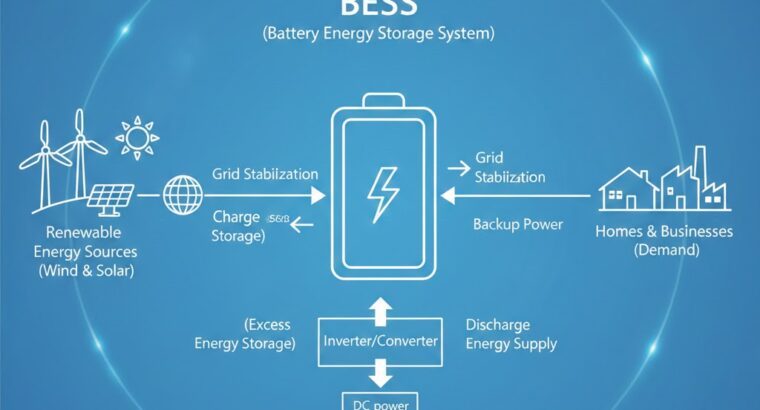
Understanding how BESS works is essential as global energy systems transition toward cleaner, more flexible, and more resilient operations. A modern Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) is not simply a collection of batteries. It is an integrated solution combining electrical engineering, power electronics, software intelligence, safety management, and thermal controls. This article provides a highly detailed look at the internal technology that allows these systems to safely store and deliver energy for homes, commercial operations, and utility-scale projects.
What Powers a Modern Storage System?
When explaining how BESS works, it’s important to view the system as an ecosystem. It includes:
- A battery stack that stores energy
- A power conversion system that manages AC/DC transformation
- A battery management system that protects cells and modules
- A thermal system that regulates temperature
- An energy management system that makes operational decisions
These subsystems work continuously to maintain efficiency, extend battery life, and ensure safe operation.
Core Components That Determine How BESS Works
1. Battery Cells and Modules
The foundation of the system is the battery chemistry—commonly lithium iron phosphate (LFP) or nickel manganese cobalt (NMC). Cells assemble into modules, which form racks, and racks populate the enclosure. Capacity, safety stability, and lifespan all depend on the chemical structure and manufacturing quality.
2. Power Conversion System (PCS)
A key part of how BESS works involves managing electricity flow. The PCS performs:
- AC/DC conversion
- Active and reactive power control
- Grid-forming or grid-following functions
- Harmonic correction
It ensures seamless energy exchange between the storage unit and the grid or load.
3. Battery Management System (BMS)
The BMS monitors voltage, current, SOC (State of Charge), SOH (State of Health), and temperature at cell, module, and rack levels. Its primary job is safety. It prevents:
- Overcharging
- Deep discharge
- Short circuits
- Thermal runaway
This system is essential to stable operation and long-term performance.
4. Energy Management System (EMS)
The EMS optimizes how energy is charged or discharged. It uses algorithms and forecasting to coordinate:
- Peak shaving
- Time-of-use optimization
- Renewable integration
- Demand response
- Backup switching
This software layer is central to controlling how BESS works within a larger energy environment.
5. Thermal Management System
Both low and high temperatures reduce battery life and operational safety. Thermal systems—air cooling, liquid cooling, or hybrid—maintain stable conditions.
How BESS Works: The Energy Flow Cycle
1. Charging Cycle
Energy from solar, wind, or the grid is converted through the PCS into DC power that charges the battery. The BMS monitors each cell and adjusts charging rates based on temperature, voltage, and internal resistance.
2. Energy Storage Phase
Once charged, energy remains stored chemically. Internal monitoring systems track changes in SOC, voltage balance, and thermal status to prevent deterioration.
3. Discharging Cycle
When the grid or load requires power, the PCS converts stored DC into usable AC. The EMS decides when and how much to discharge based on demand, cost signals, or backup requirements.
Different Configurations That Influence How BESS Works
1. AC-Coupled Configurations
Ideal for retrofits or renewable add-ons. The PCS provides isolation, and each unit operates independently.
2. DC-Coupled Configurations
Best for maximizing solar capture because PV feeds directly into the DC bus without additional conversions.
3. Hybrid Inverter Platforms
Common in residential and small commercial systems where a single device manages PV, storage, and grid connections.
Understanding the Software Layer
Software plays a major role in how BESS works today.
1. Forecasting Tools
Weather integration helps predict solar and wind generation.
2. Optimization Algorithms
The EMS decides when to discharge for maximum economic benefit or operational stability.
3. Remote Monitoring and Diagnostics
Cloud-linked dashboards allow operators to access real-time data on performance, faults, temperature, and SOC.
Operational Modes
1. Grid Services
A well-configured system can provide:
- Frequency response
- Voltage support
- Black start capabilities
- Spinning reserve replacement
2. Backup Power
When the grid fails, the system instantly supports critical loads.
3. Renewable Firming
The system smooths intermittency and stabilizes renewable output.
4. Peak Shaving
Large facilities reduce demand charges by discharging during high-load periods.
Safety Mechanisms Inside the System
Explaining how BESS works also means understanding its safety engineering:
- Cell-level protection via the BMS
- Overcurrent and overvoltage protection in the PCS
- Pre-charge circuits
- Arc detection
- Fire suppression (aerosol, water-based, or clean agent)
- Thermal barriers
- Ventilation and off-gas detection
Additionally, enclosures follow certifications such as UL 9540A, IEC 62933, and NFPA 855.
Reliability and Lifecycle Factors
System lifespan depends on:
- Depth of discharge cycles
- Temperature regulation
- Charge/discharge rates
- Chemistry type
- Software optimization
A well-tuned system can operate 10–15 years with stable performance.
How BESS Works in Each Sector
1. Residential
Provides self-consumption, backup power, and energy cost control.
2. Commercial & Industrial
Delivers demand-charge reduction, renewable integration, and microgrid support.
3. Utility-Scale
Supports grid reliability, peak generation replacement, and renewable smoothing.
Each sector uses the same core technology, but the scale, software, and control logic vary significantly.
Market Trends Shaping (2025–2030)
Key developments include:
- Shift to LFP and sodium-ion chemistries
- Larger PCS units with grid-forming capabilities
- More autonomous EMS platforms
- Standardization of safety testing
- Hybrid renewable + storage solutions
- Virtual power plants (VPPs)
- AI-based predictive maintenance
The industry is accelerating rapidly in both hardware and software innovation.
Conclusion
Understanding how BESS works requires examining every component—from the chemistry of the cells to the digital intelligence of the EMS. These systems store energy, support renewable integration, enhance grid stability, and provide backup power across residential, commercial, and utility applications. As technology advances, energy storage is becoming one of the most critical elements of a modern, flexible, and sustainable energy future.
[…] How Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) Works […]